JOINS: Join is used to combine one or more tables, from tables based on condition (Common fields). Joins are divided into four categories.
-
- Inner Join
- Left Outer Join
- Right Outer Join
- Full Outer Join
Table A and Table B, with some sort of relation specified by primary and foreign keys. The result of joining these tables together can be visually represented by the following diagram:
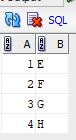
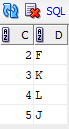
Below are the tables Table A and Table B
Types of joins:
INNER JOIN: Returns records that have matching values in both tables.
Syntax:
SELECT table1.column1,table1.column2,table2.column1,….
FROM table1
INNER JOIN table2
ON table1.matching_column = table2.matching_column;
E.g.:
Table 1: Table A
Table 2: Table B
matching_column: Column common to both the tables.
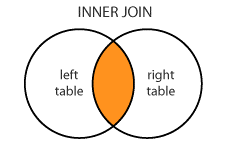
E.g.:
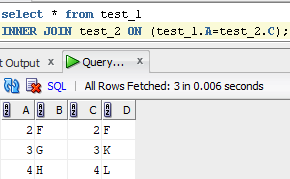
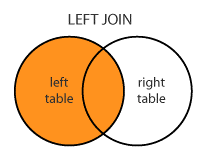
LEFT JOIN: Returns all records from the left table, and the matched records from the right table. LEFT JOIN is also known as LEFT OUTER JOIN.
Syntax:
SELECT table1.column1, table1.column2, table2.column1,….
FROM table1
LEFT OUTER JOIN table2
ON table1.matching_column = table2.matching_column;
E.g.:
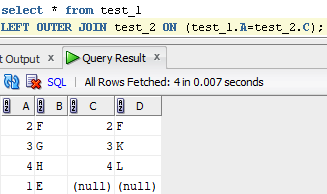
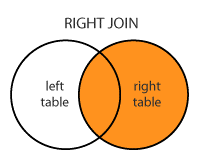
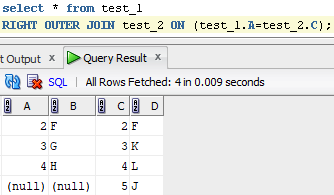
RIGHT JOIN: Returns all records from the right table, and the matched records from the left table. RIGHT JOIN is also known as RIGHT OUTER JOIN.
Syntax:
SELECT table1.column1,table1.column2,table2.column1,….
FROM table1
RIGHT OUTER JOIN table2
ON table1.matching_column = table2.matching_column;
E.g.:
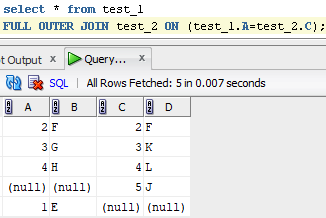
FULL JOIN: Returns all records when there is a match in either left or right table. The rows for which there is no matching, the result-set will contain NULL values.
Syntax:
SELECT table1.column1,table1.column2,table2.column1,….
FROM table1
FULL JOIN table2
ON table1.matching_column = table2.matching_column;
E.g.: