What is SaaS
As the complexity of on-premises applications, servers, storage, infrastructure needs increasing day by day, Software as a Service (SaaS) evolved to address most of these challenges and as the usage of cloud is also increasing, most of the enterprises moving towards pay-as-you-go model of service subscription.
To keep it in simple terms to understand easily, SaaS is nothing, but an application built and maintained on the cloud and can be accessed by users from anywhere and anytime without worrying too much about underlying infrastructure details.
The best example is any of the application running on one’s mobile. We do not write code of that application, do not deploy the application or maintain the application but we can access it from anywhere. Not all applications come free, but some applications need to be purchased based on the subscription model and have to pay as per the usage. The service provider will take care of the code changes, maintenance and its high availability round the clock.

-
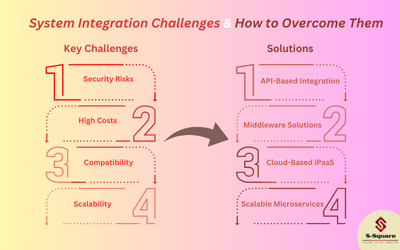
- As we can see Organizations need not spend too much time and resources in building and maintaining the applications, cost saving is a prime advantage of SaaS applications.
- As the SaaS applications are hosted on cloud and these can be accessed from web or any device that is connected to web, accessibility is always easy.
- Organizations need not worry about required skilled resources to build these applications or maintain them and can simply gain access by paying minimal cost.
- Most of the cases, SaaS applications can be accessed using free client softwares and need not purchase special softwares.
- As all these SaaS services and applications store data on cloud with adequate security in place, all the data is safeguarded all the time and can be accessed any time.
- If at all any specific requirements are there, Organizations can request for service providers to add additional functionality on top of existing services with an additional cost instead of re-inviting the whole thing.
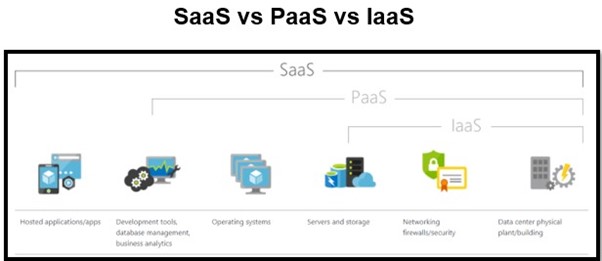
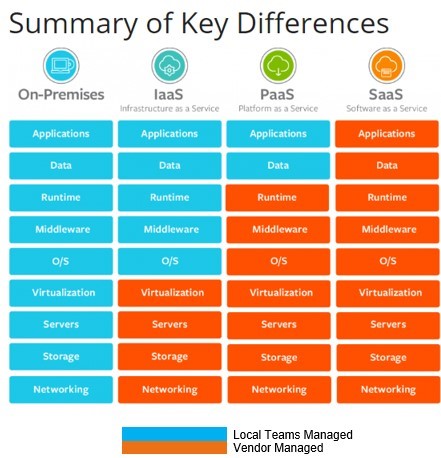
The above diagram best illustrates the major differences between SaaS when compared to Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Server (PaaS)
IaaS:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) model provides cloud platform to host the applications built locally but deployed on cloud infrastructure. These hosting platforms mainly provides servers, storage, network features and data center options. Organizations who want to maintain the development efforts locally but want to maintain the services in cloud can go for these IaaS providers.
The best scenario to go for IaaS providers is when an Organization want to have a DR (Disaster Recovery) site with minimal usage and want to have a replica of on-premises servers which helps in Continuity of Business (CoB).
The other added advantage of going with IaaS providers is when an Organization want to test some of their products without having to worry about infrastructure needs and can concentrate more on productivity.
PaaS:
In addition to the infrastructure services managed by IaaS providers, Platform as a Service (PaaS) will manage Operation System and Runtime along with infrastructure. Middleware capabilities are also given so developers can concentrate more of application development rather than concentrating on infrastructure and software / upgrades requirements.
Resources can be scaled up or down based on the requirement and multiple users can access same resources at the same time.
Let us take a look at the below diagram to understand what are the key differences between On-Premises managed services when compared to IaaS-PaaS-SaaS.