Introduction: Breaking Free from Cloud Lock-In
For years, businesses embraced the convenience of single-cloud setups, often locking themselves into proprietary ecosystems for everything — compute, storage, data analytics, AI, and more. But as companies grow, innovate, and face regulatory pressures, the risks of vendor lock-in have become impossible to ignore. From rising costs to limited flexibility and disaster recovery challenges, single-provider reliance puts businesses at risk of stagnation.
Enter multi-cloud strategies — the modern way companies of all sizes, including small businesses, are achieving business agility in cloud environments, slashing costs, enhancing resilience, and reducing vendor dependence. This blog breaks down exactly why multi-cloud flexibility is the future and how your business can benefit.
What Exactly is Multi-Cloud, and Why Should You Care?
Multi-cloud refers to a business strategy where organizations use two or more public cloud providers simultaneously to host different workloads, applications, and data. Unlike hybrid cloud, which combines on-premises infrastructure with a public cloud, multi-cloud operates entirely in the cloud — spanning platforms like AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and Oracle Cloud.
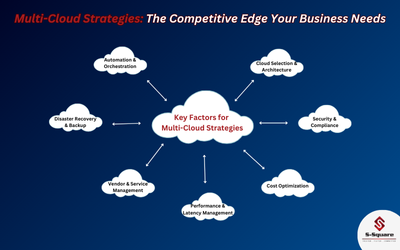
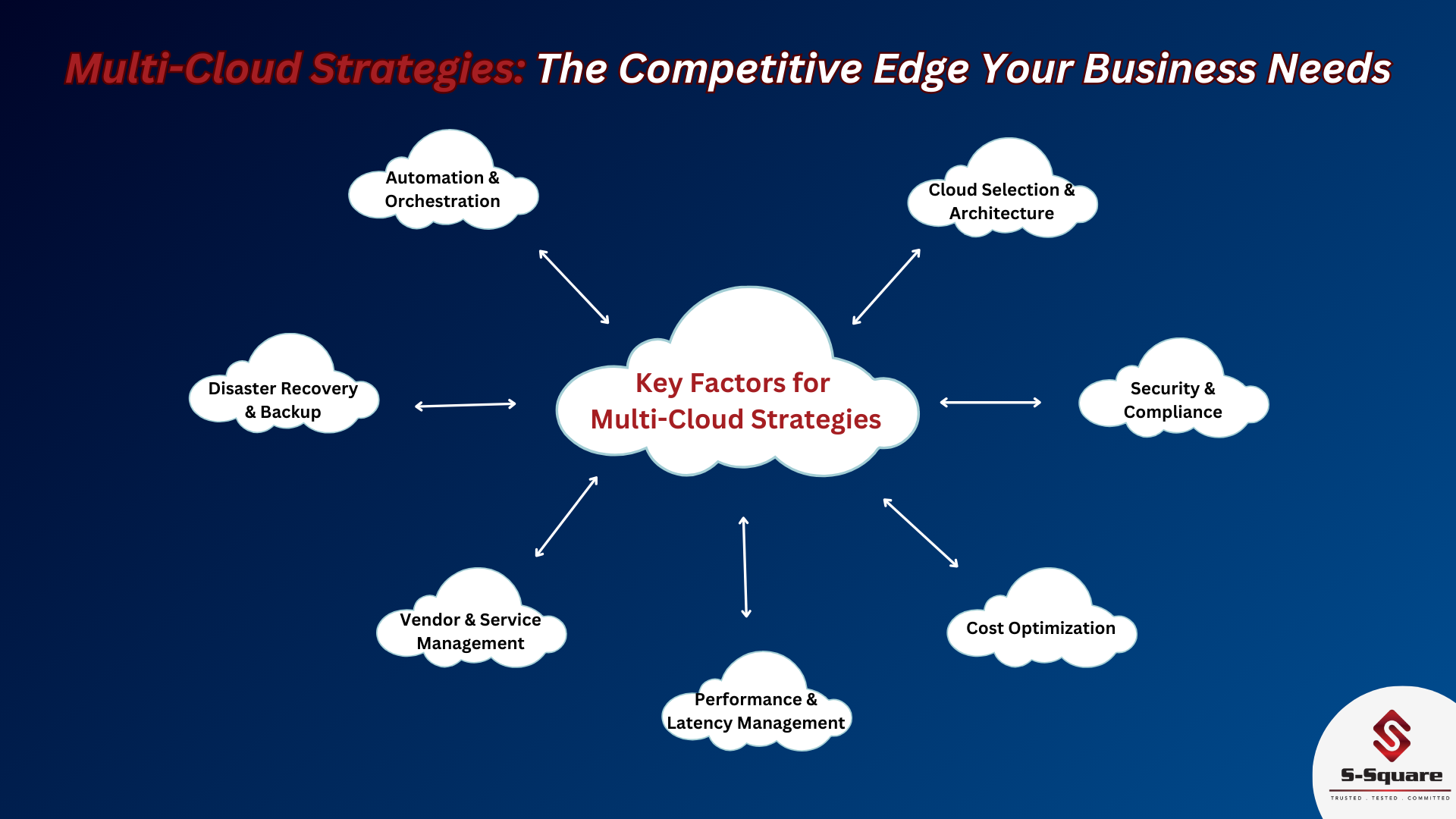
Key Benefits of Multi-Cloud
- Avoiding Vendor Lock-In Risks
One of the strongest reasons for adopting multi-cloud flexibility is to eliminate vendor lock-in risks. When your infrastructure spans multiple providers, you avoid being dependent on any single cloud’s pricing changes, feature availability, or outages. You retain negotiating power and flexibility to move or reconfigure workloads across providers. - Cost Optimization Across Providers
Different cloud platforms have varying pricing models for compute, storage, and data transfers. A strong multi-cloud cost optimization strategy allows businesses to pick the most cost-effective option for each workload — especially when paired with cost optimization tools for managing multi-cloud infrastructure that monitor, analyze, and automate savings across providers. - Technology Fit for Every Workload
Multi-cloud allows you to leverage best-of-breed technologies across platforms. For AI models, you might use Google Cloud AI services, while critical databases may reside in Oracle Cloud’s optimized environments. This flexibility ensures your architecture fits your specific business needs. - Enhanced Resilience and Disaster Recovery
No cloud provider guarantees 100% uptime. Disaster recovery plans using multi-cloud platforms ensure your business remains operational even if one provider experiences downtime. Critical systems can seamlessly failover to alternative clouds. - Compliance and Regulatory Flexibility
Different industries (healthcare, finance, and government) often face complex compliance requirements. Multi-cloud enables you to achieve compliance in multi-cloud deployments by storing sensitive data in specific compliant regions (like AWS GovCloud or Oracle’s Financial Services Cloud) while running non-sensitive workloads elsewhere.
Real-World Case Studies: Multi-Cloud in Action
Case Study 1: Infor’s Multi-Cloud Strategy with AWS GovCloud and Oracle Cloud
Challenge:
Infor, a global leader in cloud ERP software, needed to deliver services to U.S. government agencies, requiring strict adherence to federal compliance standards like FedRAMP. At the same time, they needed a reliable way to manage their own internal back-office operations using specialized ERP tools — without being locked into a single provider’s ecosystem.
Solution:
Infor adopted a multi-cloud strategy, leveraging AWS GovCloud for government-facing applications to meet stringent regulatory requirements, while utilizing Oracle Cloud for their internal ERP and financial management systems. This multi-cloud flexibility allowed Infor to:
- Maintain compliance with U.S. federal regulations.
- Optimize costs by aligning each workload to the most efficient cloud platform.
- Enhance business continuity and disaster recovery by distributing critical systems across multiple clouds.
Reference: Read the full case study on AWS
Case Study 2: Oracle’s Multi-Cloud Integration with AWS and Azure
Challenge:
Many enterprises heavily invested in Oracle databases wanted to embrace cloud modernization without completely re-architecting their core systems. These companies also needed to integrate advanced AI and analytics capabilities, which Oracle Cloud alone could not fully address. The challenge was to modernize while avoiding vendor lock-in and preserving existing Oracle investments.
Solution:
Oracle enabled seamless multi-cloud integrations where businesses could continue using Oracle databases within Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), while tapping into AWS and Azure for advanced AI, big data analytics, and application modernization. This hybrid multi-cloud strategy provided:
- Cost optimization through workload-specific placement across clouds.
- Cloud portability by decoupling databases from analytics and app layers.
- Reduced migration risk by keeping Oracle core systems intact.
Reference: Explore Oracle’s Multi-Cloud Case Studies
Case Study 3: AWS Multi-Cloud Capabilities in Action
Challenge:
As enterprises rapidly adopted multi-cloud strategies, they needed interoperability capabilities to seamlessly integrate AWS services with other providers like Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure. Enterprises wanted to take advantage of AWS’s scalability while avoiding long-term vendor lock-in risks.
Solution:
AWS enhanced its multi-cloud capabilities, including improved data portability, cross-cloud networking options, and hybrid cloud support through services like AWS Outposts and AWS Direct Connect. This enabled enterprises to:
- Retain flexibility to shift workloads between AWS and other clouds.
- Achieve compliance by distributing data across providers.
- Leverage AWS for high-performance computing while using Azure for collaboration tools or Google Cloud for AI/ML workflows.
Reference: Learn more from the AWS Multi-Cloud Capabilities Blog
How Businesses of All Sizes Benefit from Multi-Cloud Environments
Benefits to Small Businesses
Small businesses often assume that multi-cloud strategies are only for large enterprises with complex IT setups. But in reality, small businesses stand to gain significant advantages from multi-cloud environments, especially when it comes to:
- Cost Control and Flexibility
Small businesses can leverage cost optimization tools for managing multi-cloud infrastructure to automatically monitor costs and performance across providers. This helps reduce unnecessary spending and ensures they are getting the most value from every cloud service. - Best-of-Breed Technologies at Startup-Friendly Pricing
Multi-cloud allows small businesses to combine low-cost storage from AWS, cutting-edge AI in cloud computing from Google Cloud, and financial management tools from Oracle Cloud, all without committing to one vendor. - Resilient Disaster Recovery
With disaster recovery plans using multi-cloud platforms, even small businesses can affordably establish failover setups, ensuring operations continue if one cloud experiences downtime. - Avoiding Vendor Lock-In Risks from the Start
Small businesses are often highly agile, and multi-cloud helps them preserve that agility by avoiding vendor lock-in risks early. This flexibility is crucial for adapting to changing technology and customer demands.
Benefits to Medium-Sized Businesses
For mid-sized businesses balancing scalability and cost-efficiency, multi-cloud environments offer flexibility, operational control, and enhanced resilience. Mid-sized companies, especially those in regulated industries or with global operations, benefit in several ways:
- Scalability Without Infrastructure Bottlenecks
Medium-sized businesses can adopt multi-cloud flexibility to scale applications and infrastructure across multiple providers without hitting resource limits or regional service gaps. - Tailored Workload Placement for Performance and Cost
Mid-sized firms often have diverse workloads, from customer-facing applications to internal analytics platforms. Cloud portability within multi-cloud environments enables them to match each workload to the ideal cloud platform for performance, compliance, or cost savings. - Advanced Security and Compliance Management
Growing businesses facing industry regulations (HIPAA, GDPR, CCPA, etc.) can leverage zero trust security architecture for multi-cloud environments, ensuring consistent security policies across all platforms. Plus, achieving compliance in multi-cloud deployments becomes easier with unified compliance monitoring tools like Prisma Cloud. - Enhanced Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Mid-sized companies rely heavily on IT resilience to maintain customer trust. Spreading disaster recovery across multiple clouds ensures faster failovers and reduces the risk of a complete outage. - Negotiation Leverage with Providers
Unlike small businesses, medium-sized companies may spend millions on cloud services, giving them bargaining power. By using multi-cloud strategies, they can negotiate better terms with each provider, using competition to their advantage.
Benefits to Large Enterprises
Large enterprises with complex global operations face entirely different challenges — regulatory compliance across regions, massive data gravity issues, and pressure to adopt sustainable cloud practices. For them, multi-cloud becomes not just a strategy, but a necessity. Key benefits include:
- Global Performance Optimization
Large enterprises often need to distribute applications and data across multiple geographies. With multi-cloud strategies, they can host applications closer to users while optimizing data transfer in multi-cloud setups for latency, bandwidth, and cost. - Advanced AI and Big Data Analytics
Enterprises rely heavily on AI in cloud computing for everything from predictive maintenance to customer personalization. By using best-of-breed AI tools across clouds, they can train models in Google Cloud, analyze financial data in Oracle Cloud, and deploy customer apps on AWS — all seamlessly integrated into their multi-cloud fabric. - Reducing Carbon Footprints in IT Operations
With increasing ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) pressures, large enterprises are prioritizing multi-cloud strategies for reducing carbon footprints in IT operations. By choosing cloud providers with green data centers, leveraging autoscaling across clouds, and minimizing inter-cloud data transfers, they can align IT operations with corporate sustainability goals. - Cross-Cloud Compliance and Governance
Global enterprises face region-specific compliance requirements, from GDPR in Europe to data sovereignty rules in Asia. With multi-cloud flexibility, they can segment data and processes across compliant regions and use centralized compliance tools to maintain visibility and control across platforms. - Enhanced Resilience for Critical Systems
When global operations depend on continuous uptime, disaster recovery plans using multi-cloud platforms become essential. Enterprises design active-active setups across clouds, ensuring critical systems can failover instantly if any one provider experiences issues. - Negotiating Enterprise Discounts and Vendor Leverage
Large enterprises with multi-cloud flexibility often command significant negotiating leverage. By spreading their spending across providers, they can optimize pricing while retaining the freedom to shift workloads if one provider’s terms or technology roadmap no longer aligns with their needs.
AI and IoT in Multi-Cloud Setups
Best Practices for AI and IoT Integration in Multi-Cloud
- Distributed Data Storage
AI models need vast amounts of data. With multi-cloud flexibility, businesses can store IoT sensor data in AWS S3, train models using Google Cloud AI, and deploy applications on Azure Kubernetes Service. - Cross-Cloud Processing Pipelines
Best practices for integrating AI and IoT in multi-cloud setups involve building cloud-agnostic pipelines that ingest, clean, train, and deploy models across multiple platforms, ensuring portability. - AI Insights Across Platforms
With AI in cloud computing, businesses can monitor performance and costs across clouds, identifying where to optimize or shift workloads for better efficiency and agility.
Sustainable Cloud Practices with Multi-Cloud
Multi-Cloud Strategies for Reducing Carbon Footprints
- Region Selection Based on Sustainability
Providers now disclose the carbon intensity of their data centers. Businesses using multi-cloud can prioritize deploying workloads in low-carbon regions. - Resource Optimization and Autoscaling
Multi-cloud environments support automated scaling, ensuring resources only run when needed, helping reduce both costs and emissions. - Data Gravity Considerations
Multi-cloud allows businesses to store data close to where it’s processed, minimizing data transfer in multi-cloud setups and reducing unnecessary energy consumption.
Multi-Cloud Security: Achieving Zero Trust
Zero Trust Security Architecture for Multi-Cloud Environments
- Identity-Centric Security
In multi-cloud security, zero trust models enforce granular access controls based on user identity, device health, and contextual factors. - Centralized Security Management
Multi-cloud platforms benefit from centralized visibility, using tools like Prisma Cloud to manage policies across AWS, Azure, and Oracle Cloud. - Encryption and Key Management
Consistent encryption practices across providers help secure data in transit and at rest.
Conclusion: How S-Square Powers Your Multi-Cloud Success
At S-Square, we specialize in helping businesses — from small startups to large enterprises — design, deploy, and optimize multi-cloud environments that deliver real business value.
With our expertise in cloud migration, cost optimization, multi-cloud security, and compliance, we guide clients through:
-
- Vendor lock-in solutions to keep your options open.
- Cloud portability strategies that future-proof your apps.
- Sustainable cloud practices that align IT with environmental goals.
- Best practices for AI, IoT, and emerging tech in multi-cloud setups.
- Seamless disaster recovery and compliance frameworks that span all your clouds.
Whether you’re just starting your cloud journey or need to refactor your existing architecture, S-Square brings the tools, proven methodologies, and industry partnerships to make your multi-cloud strategy a success.
FAQ’S:
What are the benefits of multi-cloud strategies for small businesses?
Avoiding vendor lock-in, multi-cloud flexibility, disaster recovery, cost optimization.
How does multi-cloud improve disaster recovery plans?
Cross-cloud failover, zero trust security, business continuity.
What tools help with multi-cloud cost optimization?
Flexera, CloudHealth, Spot.io, AWS Cost Explorer.
Is multi-cloud more secure than single cloud?
Multi-cloud security, zero trust security architecture.
How does multi-cloud support sustainable cloud practices?
Carbon footprint reduction, low-carbon region selection, autoscaling.