Introduction:
The first Industrial Revolution was driven by steam power, followed by electricity in the second, and then digitization, factory automation, and robotics in the third. Now, the Fourth Industrial Revolution is being shaped by agile manufacturing practices and by intelligent computers, also known as cyber-physical systems.
Until 2014, the term “Industry 4.0” wasn’t widely known, but by 2019, it became the number 1 trending topic among manufacturing leaders and strategic thinkers. A McKinsey survey in 2019 found that 68 percent of respondents considered Industry 4.0 as a top strategic priority manufacturing in the 21st century, and 70 percent were already testing or implementing new technology.
Industry 4.0 has ushered in a transformative era of manufacturing in the 21st century, where innovative technologies intertwine with traditional industries and reshaping how businesses operate, interact, and deliver value to their customers. However, technology is only one part of the Industry 4.0 equation manufacturing in the 21st century. To succeed in this revolution, companies must focus on upskilling and reskilling efforts, and when needed, hire new talent. Other challenges for firms include adapting to disruptive technologies within the existing regulatory frameworks, managing the overwhelming influx of data, and strengthening cybersecurity measures against growing threats.
Through this blog, we will offer insightful solutions and practical strategies tailored to Industry 4.0. We will also look at how firms can utilize IT services to navigate through the IT complexities and succeed in the Industry 4.0 age.
About Industry 4.0
The Fourth Industrial Revolution builds upon the innovations of the Third Industrial Revolution, which brought computers, electronics, and the Internet and lasted from the 1950s to the early 2000s. Industry 4.0 takes these innovations further manufacturing in the 21st century, driven by disruptive technologies across the value chain. Key ones include:
- Connectivity, Data, and Computational Power: Cloud technology, the Internet, blockchain, and sensors.
- Analytics and Intelligence: Advanced analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence.
- Human-Machine Interaction: Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), robotics and automation, Digital Twins, and autonomous guided vehicles.
- Advanced Engineering: Additive manufacturing (like 3D printing), renewable energy, and nanoparticles.
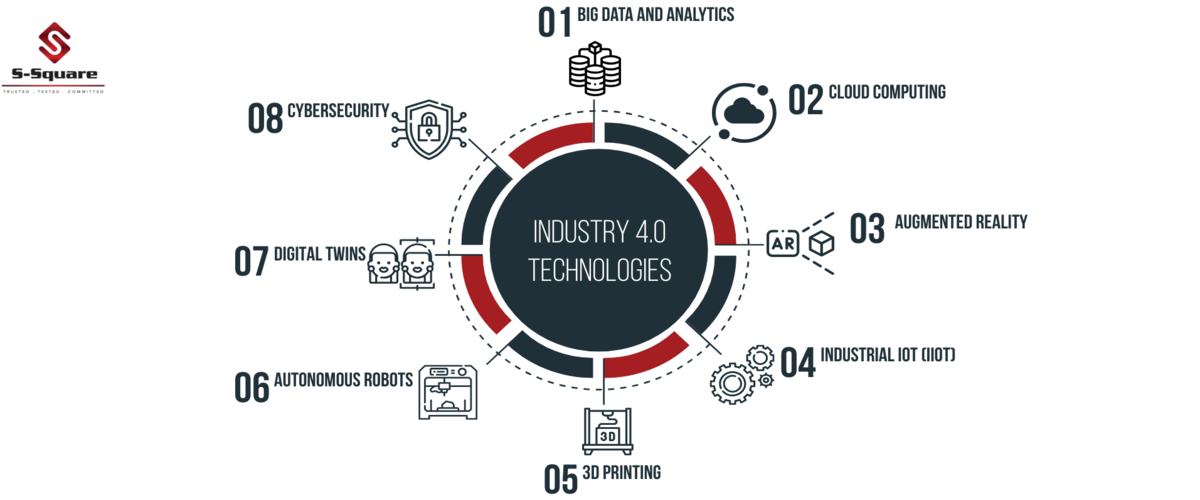
Industry 4.0 technologies
Industry 4.0 introduces several transformative technologies that reshape how businesses operate and interact. Key ones include:
Big Data and AI Analytics
Industry 4.0 leverages Big Data collected from various sources, including Internet of Things (IoT) devices and customer data. AI-powered analytics offer real-time insights, enhancing decision-making and automation.
Cloud Computing
Cloud technology forms the foundation of Industry 4.0, enabling AI, the Internet of Things (IoT), and real-time communication for cyber-physical systems.
Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital content in real environments, aiding tasks such as maintenance, training, and quality assurance.
Industrial Internet of Things (Internet of Things (IoT))
Internet of Things (IoT)’s sensors and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags provide real-time data from devices, facilitating smoother supply chains, product design, and inventory management.
Additive Manufacturing/3D Printing
3D printing/Additive manufacturing offers applications from rapid prototyping to distributed manufacturing, allowing on-demand production and diverse material usage.
Autonomous Robots
Autonomous robots perform tasks with minimal human intervention, driven by AI, sensors, and machine vision, enhancing precision and automation.
Simulation/Digital Twins
Digital twins simulate real-world systems using Internet of Things (IoT) data, improving understanding, analysis, and maintenance of industrial processes and products.
Cybersecurity in Industry 4.0
The connectivity of Industry 4.0 demands robust cybersecurity measures, involving technologies like Zero Trust architecture, machine learning, and blockchain to prevent data breaches and disruptions.
Industry 4.0 Use Cases and Benefits
The digital transformation brought by Industry 4.0 triggers both cultural and operational shifts. By connecting individuals, data, and assets, it introduces a realm of optimization opportunities. Here are examples of how Industry 4.0 solutions enhance efficiency, visibility, and sustainability across manufacturing and supply chains:
Predictive Maintenance
Integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and data analytics empowers manufacturing businesses to monitor equipment health in real-time. Predictive maintenance algorithms identify potential failures beforehand, enabling proactive processes that can reduce downtime by up to 50% and extend asset lifespan by up to 40%.
Supply Chain Optimization
Industry 4.0 offers end-to-end visibility throughout the global supply chain. With real-time data from suppliers, inventory, production schedules, customer demand, and internal teams, you can optimize logistics, balance supply and demand, enhance order fulfilment, and improve overall supply chain and manufacturing efficiency.
Agile Manufacturing
AI and advanced analytics allow real-time customer insights and feedback analysis from sources like social media and customer support interactions. This data guides R&D teams and product designers in identifying consumer preferences, pain points, emerging trends, etc.
Quality Control and Defect Detection
Utilizing Internet of Things (IoT) devices and machine learning algorithms, you can collect real-time data from production lines, enabling continuous monitoring of the manufacturing process.
Circular Economy Practices
Industry 4.0 supports circular economies by reducing waste and optimizing material reuse, refurbishment, and recycling. Leveraging Big Data analytics and Internet of Things (IoT) networks, you can track product lifecycles, implement reverse logistics, and enhance resource recovery. AI-powered advanced analytics aid in designing products that are sustainable, resource-efficient, and easily recyclable.
Carbon Footprint Monitoring and Optimization
Industry 4.0 technologies enable real-time data collection and analysis of energy consumption, transportation emissions, and carbon footprint contributors.
Empowering Manufacturers in the Industry 4.0 Era: S-Square’s Comprehensive Solutions
As the manufacturing landscape evolves rapidly within the Industry 4.0 age, S-Square, a leading IT services firm recognizes the growing challenges that manufacturing firms face in scaling efficiently and embracing data-driven approaches. Traditional transformation strategies are no longer sufficient to meet the demands of this dynamic environment. Our distinctive approach, combining domain-focused advisory services and strategic consulting, offers manufacturing clients the tools to fully leverage the potential of digitalization.
Our key services include:
Advanced Manufacturing Solutions
Our custom manufacturing services, coupled with industrial reporting tools, optimize warehouse management, and enhance enterprise asset management.
Data-Driven Insights
We enable manufacturers to leverage insights and intelligence by automating workflows, digitizing processes, and harnessing the power of customer and digital analytics.
Digital Transformation Expertise
S-Square facilitates the transition to digital manufacturing through Smart Internet of Things (IoT) solutions, engineering and R&D digitization, and platform modernization.
Optimized IT Operations
Our services encompass application management, including Nextgen EMS, modernization, implementation, and support, along with DevOps integration.
Cloud Empowerment and Analytics
We assist in crafting effective cloud strategies, managing data assets, and integrating advanced analytics and business intelligence to drive informed decision-making.
Explore our Manufacturing and Distribution page for more information
Conclusion:
Manufacturing in the 21st century is driven by Industry 4.0 and it symbolizes a fundamental change, breaking down barriers and fostering interconnectedness between various systems and processes. This allows organizations to realize many benefits such as operational efficiency, sustainability and swift decision-making through real-time data utilization. Amidst a competitive and rapidly changing environment, Industry 4.0 not only enhances efficiency but also empowers adaptability. By embracing this evolution, manufacturing entities can invite innovation and an interconnected approach to navigate success in the 21st century and beyond.